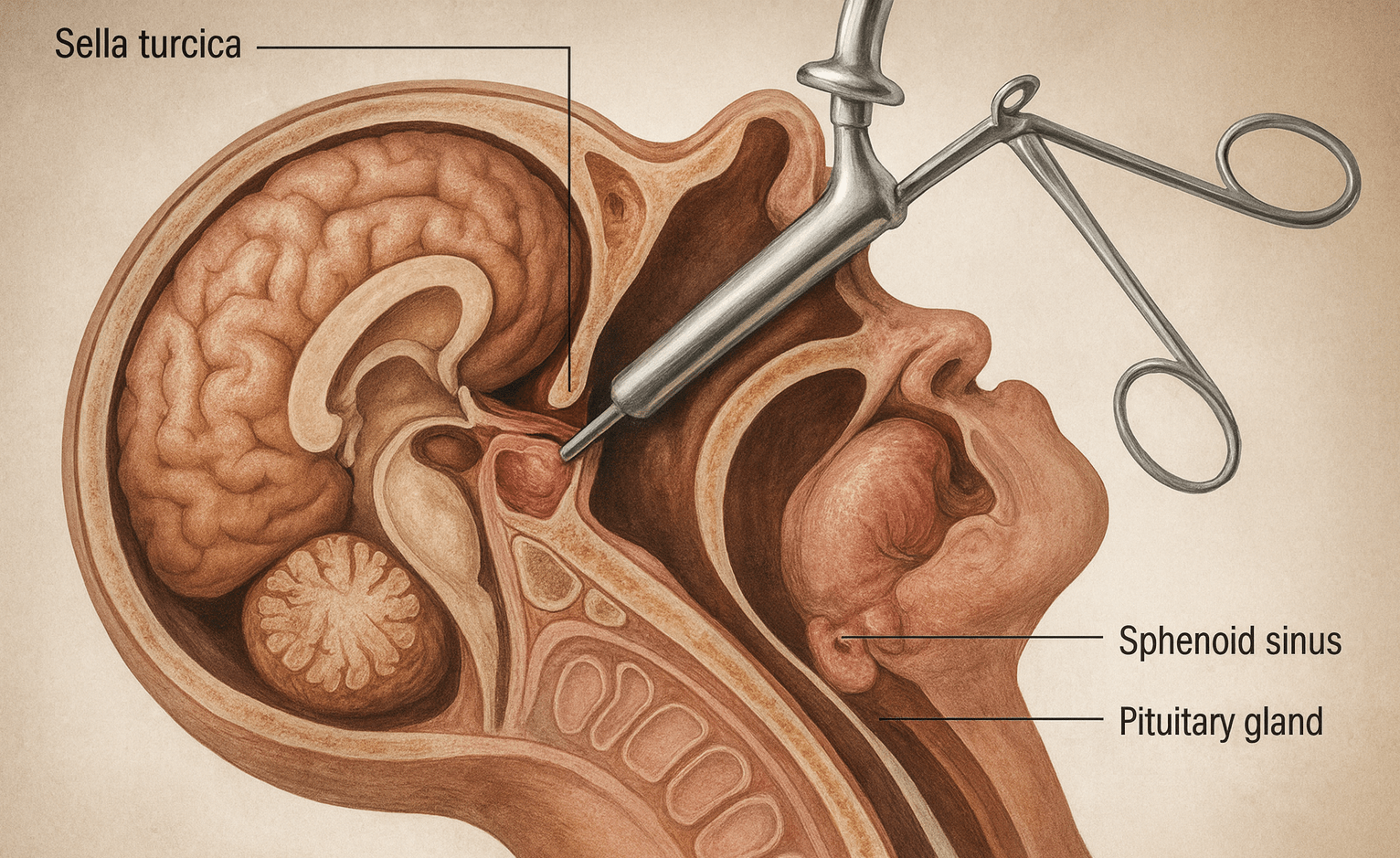
What is a Transphenoidal Hypophysectomy?
Transsphenoidal hypophysectomy is an effective neurosurgical technique for removing pituitary tumors, and other intrasellar tumors, with minimal morbidity and hospital stay.
In addition to improvement in endocrine function, it also reverses the pressure effects on the pituitary gland and adjacent structures — such as optic nerves.
To perform a transsphenoidal hypophysectomy, our neurosurgeons:
- Places you in a semi-reclined position with your head stabilized
- Makes several small incisions under your upper lip and the front of your sinus cavity
- Inserts a speculum to keep your nasal cavity open
- Inserts an endoscope to view projected images of your nasal cavity on a screen
- Inserts special tools, such as a type of forceps called pituitary rongeurs, to remove the tumor and part or all of the pituitary gland
- Uses fat, bone, cartilage, and some surgical materials to reconstruct the area where the tumor and gland were removed
- Inserts gauze treated with an antibacterial ointment into the nose to prevent bleeding and infections
- Stitches the cuts in the sinus cavity and on the upper lip with sutures
Am I a Candidate?
A hypophysectomy is a surgery done to remove the pituitary gland.
Hypophysectomy is done for a number of reasons, including:
- Removal of pituitary tumors
- Removal of craniopharyngiomas, tumors made of tissue from around the gland
- Treatment of Cushing’s syndrome, which happens when your body is exposed to too much of the hormone cortisol
- Improving vision by removing extra tissue or masses from around the gland
Only part of the gland may be removed when tumors are removed.
Schedule an e-consult here to learn more about your candidacy for transsphenoidal hypophysectomy.
What to Expect from a Transsphenoidal Hypophysectomy Procedure
Endoscopic transphenoidal hypophysectomy would require the full set of instruments for sinus surgery, along with a high-speed drill and homeostatic agents like gelatin with thrombin. The microscopic approach would require a maxillofacial instrument set with a Hardy self-retaining bivalve speculum. Image guidance navigation (IGN) system is preferable in revision procedures, parasellar extension, or cases with distorted anatomy. Intraoperative MRI is of significant benefit in pituitary surgery, as it provides updated images showing the change in tumor volume, the dura, and normal pituitary.
Types of tests to determine if a transphenoidal hypophysectomy surgery is needed:
- Blood Tests. Blood tests help doctors detect many hormonal abnormalities associated with pituitary tumors.
- Vision Tests. Some pituitary tumors can press on nerves that lead from the eyes to the brain, causing vision problems.
- MRI Scans
- PET Scans
Conditions Transphenoidal Hypophysectomy Resolves
Our specialized neurosurgeons often recommend and perform transphenoidal surgery to treat pituitary adenomas.
Transphenoidal Hypophysectomy Aftercare & Positive Recovery
- For one to two days, you’ll walk around with the help of a nurse until you’re able to walk on your own again. The amount that you pee will be monitored.
- For the first few days after surgery, you’ll undergo blood tests and vision tests to make sure your vision hasn’t been affected. Blood will likely drain from your nose periodically.
- After leaving the hospital, you’ll return in about six to eight weeks for a follow-up appointment. You’ll meet with your doctor and an endocrinologist to see how your body is responding to possible changes in hormone production. This appointment may include a head scan as well as blood and vision tests.
Until directed, our neurosurgeon office also recommends patients avoid doing the following:
- Blowing our cleaning your nose
- Bending forward
- Lifting objects heavier than 10 pounds
- Swimming, taking a bath, otherwise placing your head under water
- Driving or operating large machinery
A hypophysectomy takes one to two hours. Some procedures, like stereotaxis, may take 30 minutes or less.

